Bacterial Population Growth Curves Typically Include Which of the Following
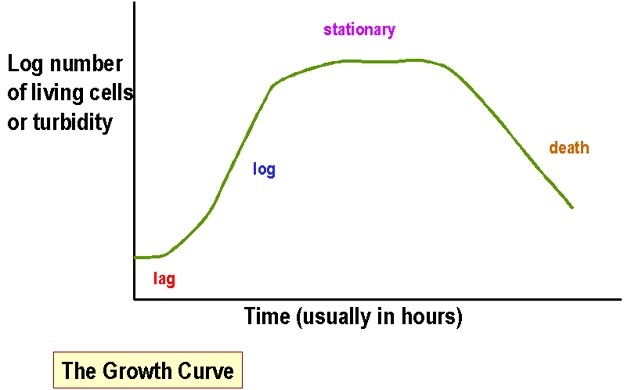
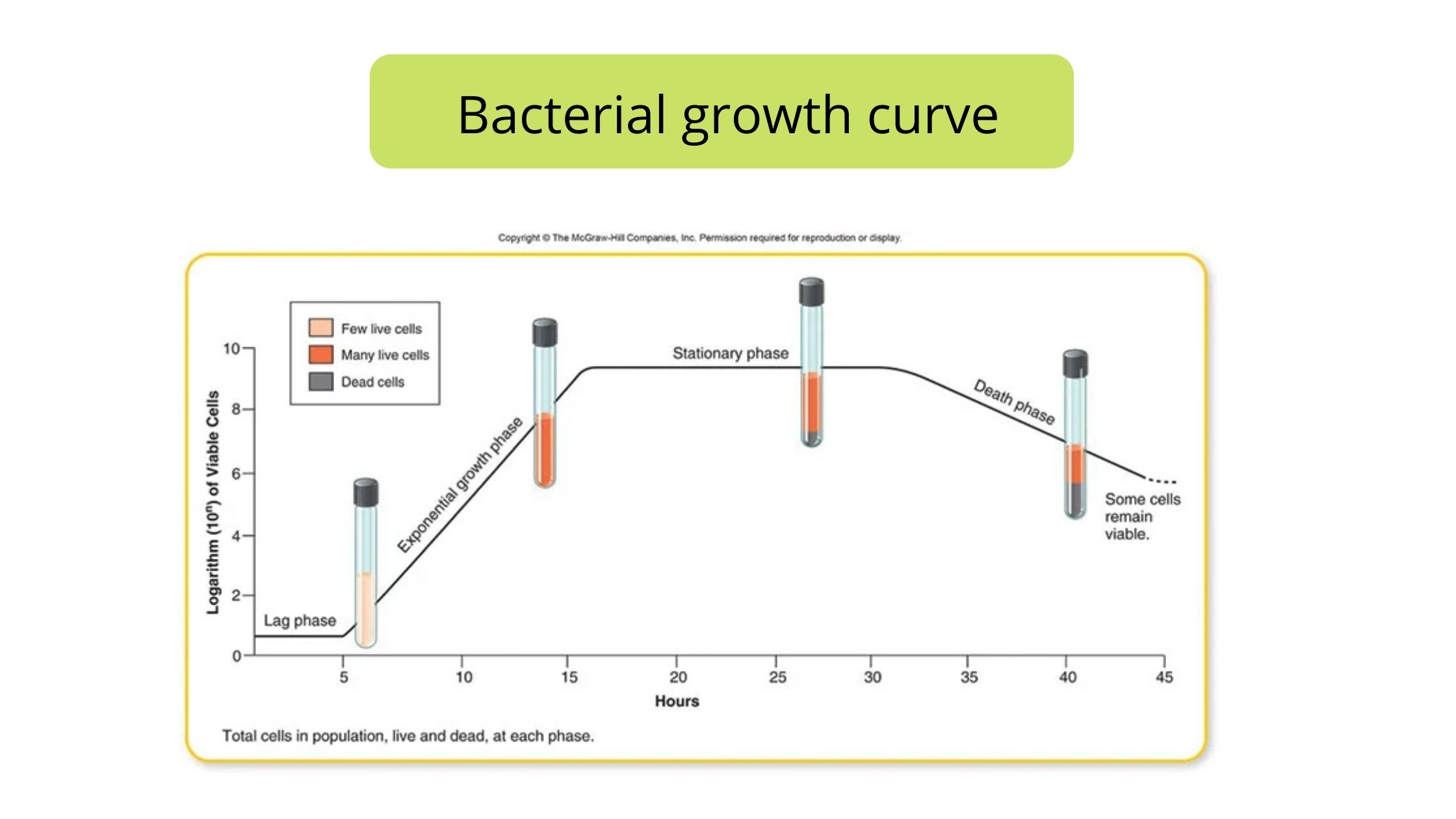
There are four distinct phases of the growth curve. The lag phase the exponential or log phase the stationary phase and the death or decline phase.
Bacterial Growth Curve Phases Significance Microbe Online
Lag exponential log stationary and death.

. U Most bacteria divide every 1 to 3 hours. Log phase or exponential phase. It takes some time to multiply.
The lag phase the log or exponential growth phase the stationary phase and the death phase. The growth rate can be expressed in a simple equation that combines the birth and death rates into a single factor. The lag phase the.
Microbial Growth Growth of Bacterial Cultures Bacterial Division. After a liquid culture broth is inoculated the multiplication of bacteria does not start immediately. Growth is by geometric progression.
The log phase is generally quite rapid and puts the bacterial cells in a vulnerable position. The Bacterial Growth Curve. Notice that when N is almost zero the quantity in brackets is almost equal to 1 or KK and growth is close to exponentialWhen the population size is equal to the carrying capacity or N K the quantity in brackets is equal to zero and growth is equal to zeroA graph of this equation logistic growth yields the S-shaped curve bIt is a more realistic model of population growth.
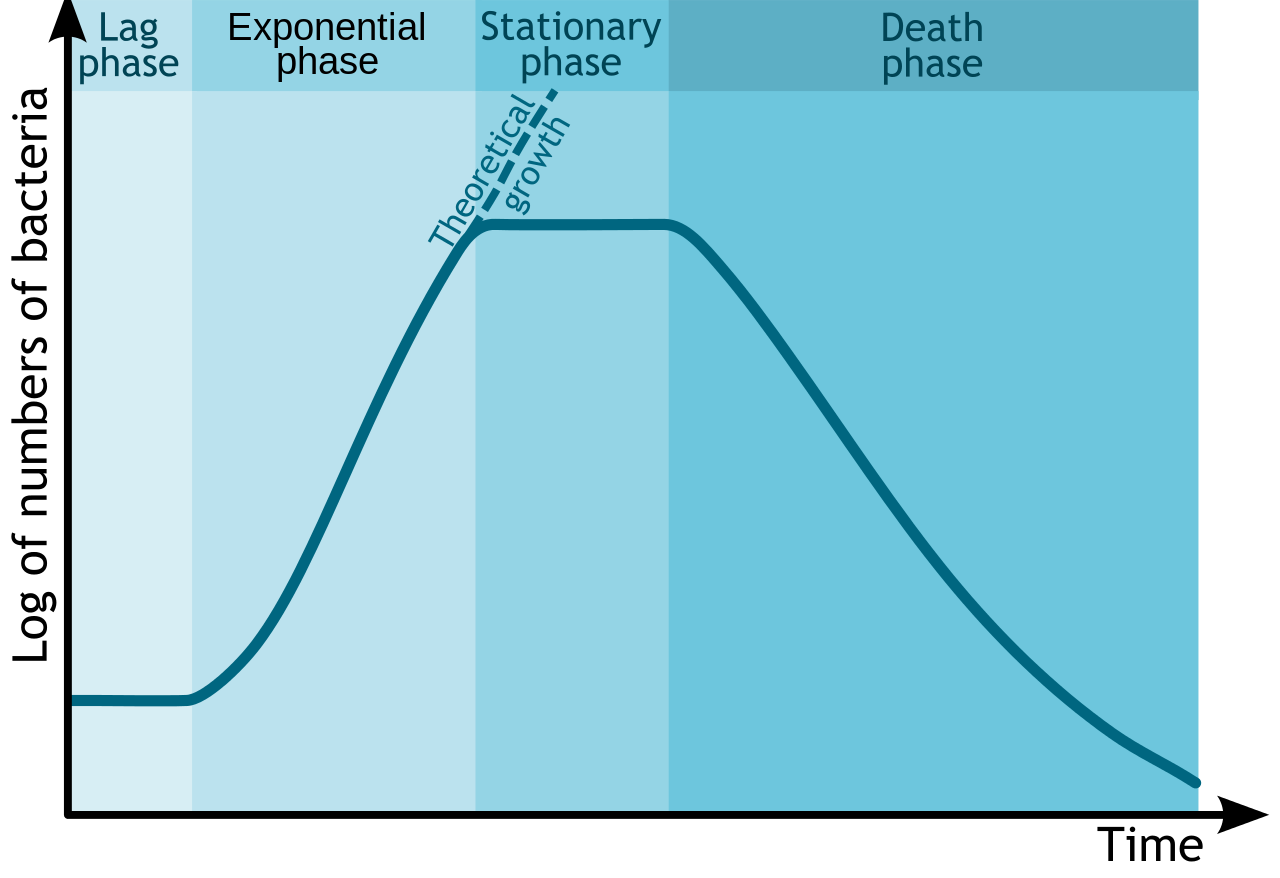
During batch culture a typical bacterial growth curve shows five distinct phases of growth. The bacterial growth curve represents the number of live cells in a bacterial population over a period of time. Generation time varies considerably.
The log phase is whats happening when your sour cream goes from white to green overnight. During this phase there is no increase in cell number. The typical growth curve for a population of cells can be divided into several distinct phases called the lag phase log phase stationary phase and death phase.
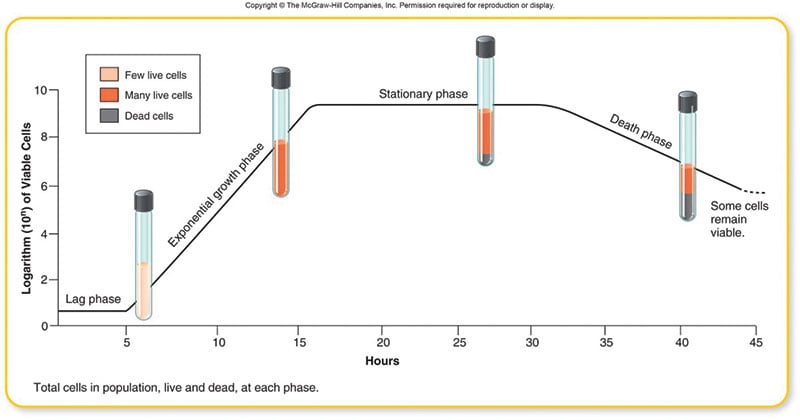
A curve on a graph that shows the changes in size of a bacterial population over time in a culture. The third phase of bacterial cell growth is called the stationary phase. Additionally this growth curve can yield generation time for a.
The exponential or log phase is a time of exponential. Due to rapid cell division bacteria have smallest size in this phase. This is called exponential growth.
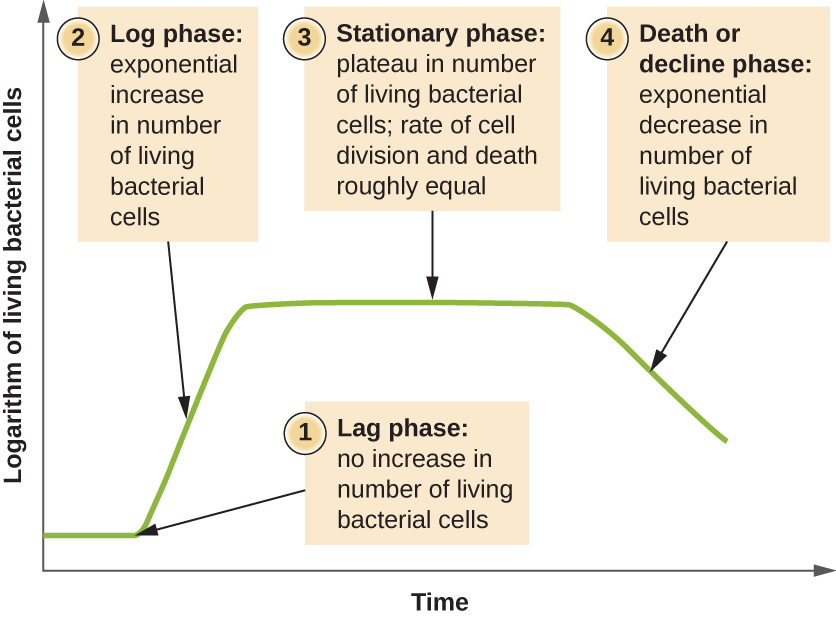
In the laboratory under favorable conditions a growing bacterial population doubles at regular intervals. Occurs mainly by binary fission. It has been determined that in a closed system or batch culture no food added no wastes removed bacteria will grow in a predictable pattern resulting in a growth curve composed of four distinct phases of growth.
During the log phase the size of the bacterial colony increases dramatically. Coli divides every 20 minutes. Bacterial growth curveKinetic Curve.
In this phase all bacteria are in their rapid stage of cell division and show balanced growth. Explain the different phases of growth of bacteria. Or 2 0 2 1 2 2 2 32 n where n the number of generations.
This is the initial phase. In the growth curve of a bacteria population the bacteria are rapidly increasing in number in the a. Standard bacterial growth curve A curve on a graph that shows the changes in size increase in number of a bacterial population over time in a culture describes various stages of growth a pure culture of bacteria will go through beginning with the addition of cells to sterile media and ending with the death of all of the cells present.
In the laboratory they are grown in a closed system or batch culture system in a predictable pattern where no foods are added and no wastes are removed resulting in a growth curve consist of four distinct phases of growth. The initial phase is the lag phase where bacteria are metabolically active but not dividing. The bacterium starts utilising the components of the media and it will increase in its size and cellular mass.
This phase is characterized by. A few bacterial species reproduce by budding. This process could be modelled using the Fisher-Kolmogorov equation 1 where n x t is the population density of bacteria in space and time r is the maximal growth rate D is a diffusion constant that accounts for bacterial motility and K represents a maximal population density.
Generation TimeTime required for a cell to divide and its population to double. Lag log exponential stationary and death phases. Phases of Bacterial Growth Curve.
In reality exponential growth is only part of the bacterial life cycle and not representative of the. Death phase when cells lose viability. Lag phase the delay before the start of exponential growth.
This bacterial growth curve reflects the events in bacterial population when they are grown in a closed system of microbial culture of fixed volume ie. In autecological studies the growth of bacteria or other microorganisms as protozoa microalgae or yeasts in batch culture can be modeled with four different phases. The dynamics of the bacterial growth can be studied by plotting the cell growth absorbance versus the incubation time or log of cell number versus time.
The growth rate of a population is largely determined by subtracting the death rate D number organisms that die during an interval from the birth rate B number organisms that are born during an interval. Exponential phase where cell division proceeds at a constant rate. O The growth of a bacterial population is ultimately limited by factors such as depletion of nutrients concentration of waste products and antibiotics Within physiological limits bacterial growth is usually positively correlated with increase in temperature Different bacterial species typically require very similar conditions of moisture pH.
The bacterial growth curve shows the following four distinct phases. Lag phase A log phase or exponential phase B stationary phase C and death phase D. 1 2 4 8 etc.
The study of bacterial growth is done since they are started to grow in the lab. A bacterial population follows a characteristic growth curve which has four phases. During this phase bacteria divides continuously at constant rate and the number of bacteria increase exponentially.
The time between inoculation and beginning of multiplication is known as lag phase. Rather bacteria are preparing for reproduction and synthesizing DNA and various. Stationary phase when conditions become unfavorable for growth and bacteria stop replicating 8 70 78.
The curve thus obtained is a sigmoid curve and is known as a standard growth curve.
How Microbes Grow Microbiology

Bacteria Growth Of Bacterial Populations Britannica
Microbial Growth General Microbiology

An Introduction To Population Growth Learn Science At Scitable
Bacterial Growth Curve And Its Significance

Typical Bacterial Growth Curve Ln Od Is Plotted Versus Time The Download Scientific Diagram
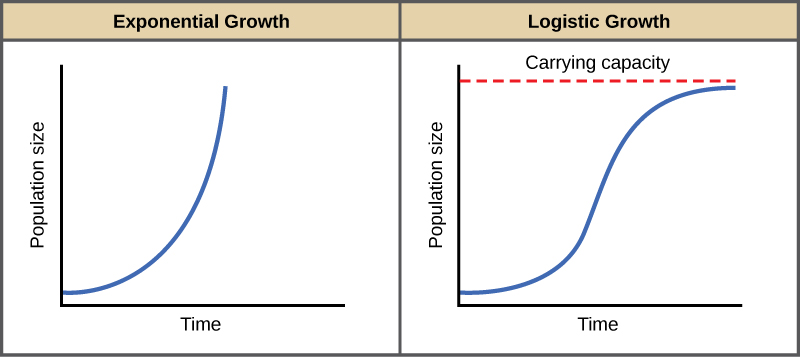
Environmental Limits To Population Growth Biology For Majors Ii

What Is Carrying Capacity Population Education

Population Growth Regulation Geometric Logistic Exponential Exponential Growth Geometric

Bacterial Growth Curve And Different Phases

Puc18 19 Vector Dna Molecule Microbiology Molecules

Typical Bacterial Growth Curve Ln Od Is Plotted Versus Time The Download Scientific Diagram


/MacroscaleMicroscaleModelGraphs-ExponentialGrowth-5769372-56a6ab923df78cf7728fa255.png)

Comments
Post a Comment